Printed Electronics
Inkjet printing is a material-conserving deposition technique used for liquid phase materials. The process essentially involves the ejection of a fixed quantity of ink in a chamber, from a nozzle through a sudden, quasi-adiabatic reduction of the chamber volume via piezoelectric action. The potential end products include flexible displays, power sources, large-area user interfaces, radio frequency identification (RFID) tags, spoilage indicators on consumer food packages, functional touch-surfaces, disposable diagnostic sensors, etc.

Synthesis of nanoparticle ink
In the ink-jet patterning process, conductive ink, which consists of metal nanoparticles and solutions, is an important factor in improving the properties of printer patterns, and even the processes. With conductive ink, when the metal particles are coarse and rough, nozzle clogging and poor patterning in the ink-jet process occurs. Recent studies have focused on the synthesis of metal nanoparticles such as, Au, Ag and Cu nanoparticles. In our lab, copper, silver and gold complex ion inks were synthesized using the modified electrolysis process.

Improvement of adhesion
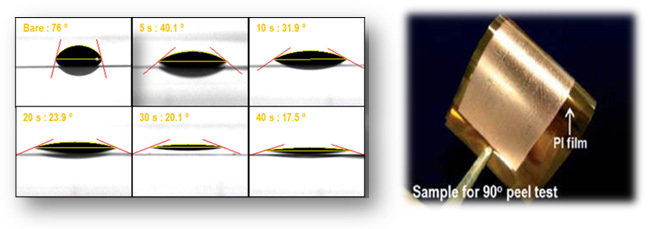
Many factors such as ink, substrate, and jetting method affect the outcomes of ink-jet printing. In particular, appropriate interactions between ink and substrate are important to successfully form continuous lines with the desired width and shape on substrates. Various methods including corona discharge, ultraviolet irradiation, electron bombardment, and plasma treatments have been used in order to modify the surfaces of substrates. We have pursued the improvement of adhesion between the substrate and the ink by silane coupling agent as an adhesion promoter and surface treatment for increasing the hydrophilicity.
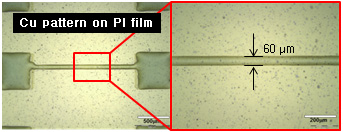
Fine pattern
For displacement of photolithography, ink-printing needs to fine pattern. Recently, many researches are proceeded to form the fine pattern. We have studied the formation of fine pattern by controlling the cartridge nozzle size, surface treatment and so on.
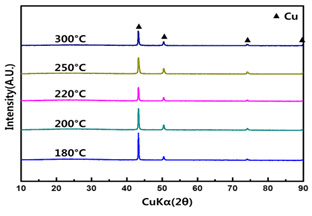
Low sintering temperature
Conductive materials that are suitable for inkjet printing can be particle based. Sintering takes place at a higher temperature when all the organic material has been burnt off and neaks begin to form between particles. However, high sintering temperature is difficult to apply flexible substrate. So, low sintering temperature is the key. We have studied the sintering methods such as laser sintering, pulsed light sintering, microwave sintering, chemical sintering and plasma sintering to overcome some of the drawbacks related to conventional oven sintering.